Google Data Scientist Interview Guide

Categories
The purpose of this article is to give you an insight into the Google data scientist interview process, the skill sets required, and most importantly, the kind of questions asked.
Introduction
What began as a small research project by two PhD students is now a household name in every corner of the world. The rapid growth of Google over the past few years has led them to explore many different opportunities in the tech industry and has made them one of, if not the biggest companies in the world right now.
The core product of Google has always been the ever-powerful search engine, however, their recent focus on providing Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) products to millions of people across the globe has changed the way in which data is collected and analyzed. Productivity services such as Google Docs, Sheets and Slides, the most popular email service Gmail, the scheduling service Google Calendar, the cloud storage service Google Drive and the ever-improving navigation service Google Maps are some of the major services which work with several million bytes of data every single second. Playing around with all this data requires a lot of expertise in the relevant field and the zeal to improve the analytics even further.
Google plays a vital role in the data science industry in the current scenario, along with the other tech giants Facebook, Amazon, Apple and Netflix. These five companies are collectively called as FAANG and have completely revolutionized the way in which the massive amount of data that is being generated every single second can be harvested, analyzed and made available for the growth and betterment of millions of people across the world.
In this article, we will have a detailed look at how Google conducts its interviews for the data science positions. The different types of Google data science interview questions are covered as well as a few tips and tricks to face these interviews. If you are interested in landing your dream job as a data scientist at Google, look no further; delve right into these questions and start building your data science career right here at StrataScratch.
Methodology and Analysis of Google Data Science Interview Questions
Earlier in this series of blogs here at StrataScratch, we covered the complete analysis of more than 900 questions collected from 80 different companies over the past 4 years. We noticed that Google is one such company which focuses heavily on their interviews to be of high quality and uses a variety of metrics to identify the perfect candidate for their Data Scientist role.
We have collected 32 interview questions for Google from various sources such as Glassdoor, Indeed, Reddit and the Blind App; these are analyzed with respect to the different types of questions that are available as well as the number of such questions that are usually asked in the interviews.
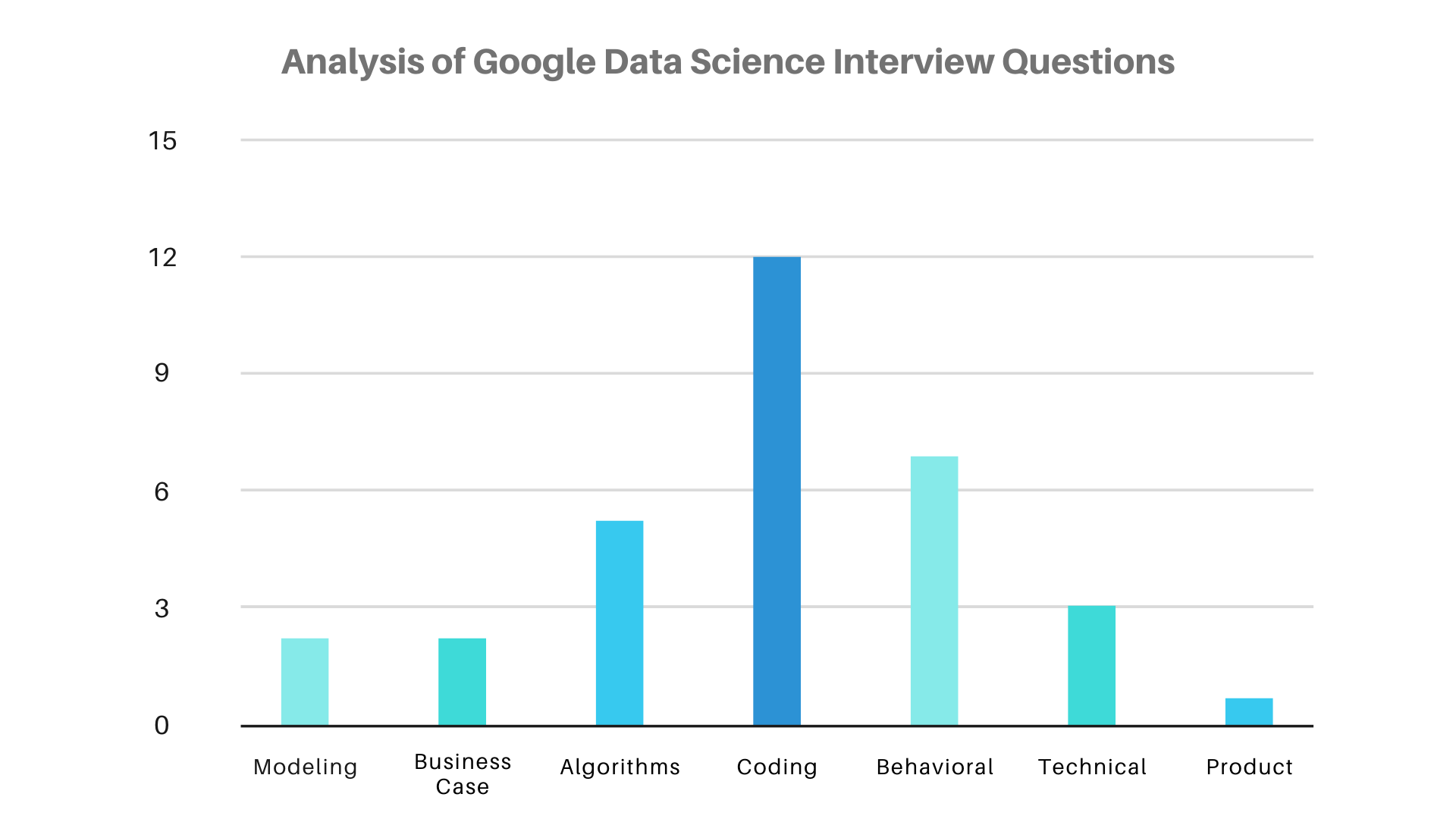
The chart above shows the different types of questions that are asked in the Google Data Scientist interviews. We notice that there is a heavy emphasis on coding skills as well as algorithmic skills that are absolutely necessary for any data scientist.
In the data set of 32 questions that were collected and analyzed, 20 of those questions (more than 60% of the total!) were based on coding and/or algorithms, which shows the importance of technical skills that are necessary for any aspiring data scientist.
Furthermore, there is quite a lot of interest in asking questions which are either miscellaneous or behavioral in nature. These questions are usually asked to test the jovial nature of the candidate, and sometimes even to check if the candidate has good communication skills to work in an ever-increasing, fast-paced social group of employees at Google.
There is not a lot of importance given to business case studies, modeling-based questions and product sense questions. This may be due to the fact that most Google products are based on their services which change from time to time based on the situation. Regardless, the candidate would less likely be hired just on the basis of doing well in these types of questions. Technically-sound candidates are more likely to be hired based on their technical skills, and are sometimes not asked any behavioral questions in their interviews.
Data Scientist Interviews at Google
Google follows an extremely rigorous set of steps in order to hire the perfect candidate for their prestigious organization. These steps include self-reflection, searching for the job, preparing a resume tailored to the job description, attending the interviews and finally, receiving the job offer.
These interviews can be strenuous for any aspiring entry-level candidate or even for a seasoned professional in the industry; thus, we have broken down the several categories of questions that are asked in the Google Data Scientist interviews, which we hope makes it a little bit easier for you to crack them.
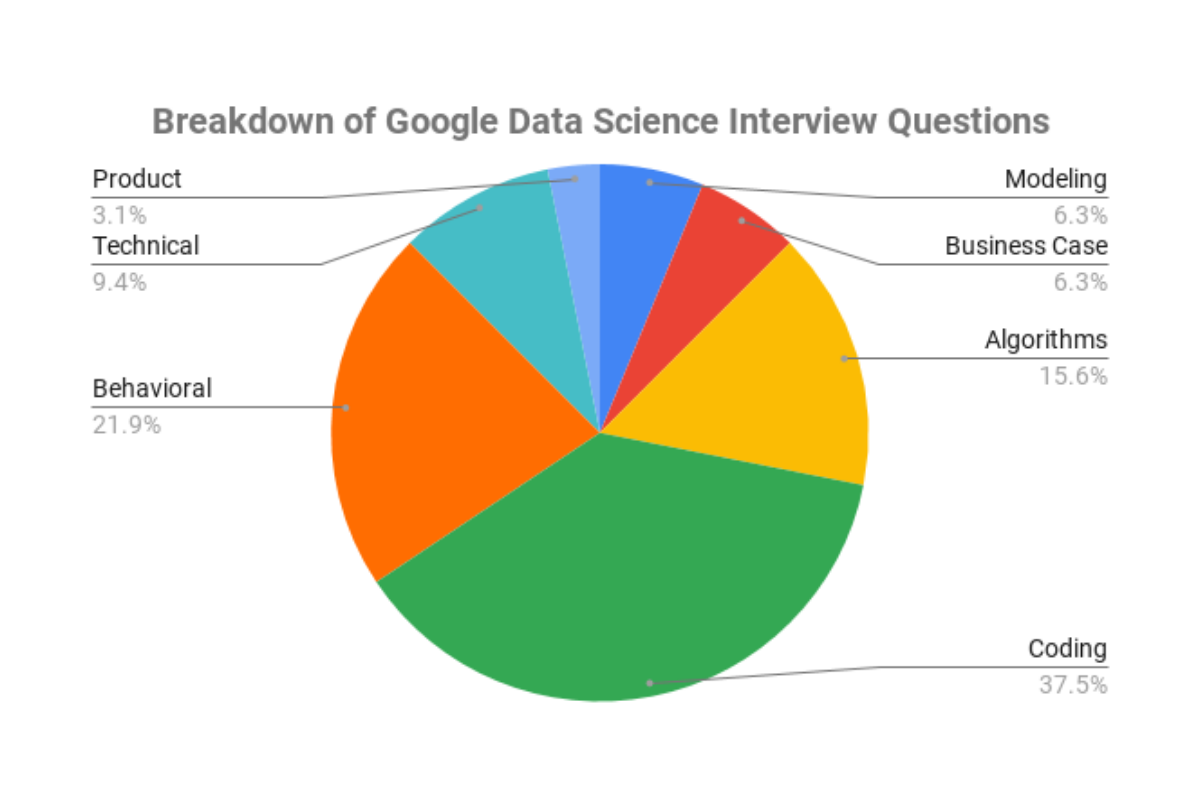
The different categories of questions that are usually asked in the Google Data Scientist interviews are given in the chart below.
Modeling
Modeling-based questions are usually based on the statistical and/or mathematical concepts that you would have studied earlier. These questions may be given on modeling concepts such as feature selection, probability distribution, Gaussian model, Lasso Ridge model, and so on.
It can be observed from the chart above that modeling-based questions account for approximately 6.3% of the total number of questions that are asked during the Google Data Scientist interview. Although this is not a very large proportion, it still plays a vital role in securing that role as a Data Scientist at Google.
A few examples of modeling-based questions are given below:
- “Why use feature selection? If two predictors are highly correlated, what is the effect on the coefficients in the logistic regression? What are the confidence intervals of the coefficients?”

A possible answer to the question can be found here on our platform.
- “Describe Lasso and Ridge regressions and Optimization.”
- “What is the difference between K-mean and EM?”
These types of questions can be tackled by thoroughly understanding the concepts behind the important statistical models.
Business Case
Business case type of questions are quite often asked in data science interviews to gauge the candidate’s ability to quickly come up with a solution, which may or may not be correct, but is conforming to the business case itself.
These types of questions are very rarely asked in Google Data Scientist interviews, however, these are very important for someone who has an avid interest in working with the business aspect of data science. Business-case questions account for approximately 6.3% of the total number of questions asked in a Google Data Scientist interview, as shown in the chart above.
A few examples for business case type of questions are given below:
- “How many cans of blue paint were sold in the United States last year?”
A possible answer to this question can be found here on our platform.
- “If you were tasked with increasing Gmail’s user base, what steps would you take to make that happen?”
- “Do you think Google should be charging for its productivity apps (Google Docs, Google Sheets, etc.)? Why or why not?”
As you can see, the question does not have anything to do with technical knowledge or coding skills. It is merely used to test the candidate’s quick thinking ability and approximation skills, which can be used for purposes such as budgeting in the business.
Algorithms
This subsection and the next one, coding, are probably the ones that you are most interested in. We shall delve straight into the numbers. These questions mostly test the ability to come up with solutions to standard questions on-the-go. These may be asked with respect to probability, statistics or standard algorithms used in data science.
Our analysis shows that approximately 15.6% of the data science questions asked are based on algorithms. This attests to the fact that Google is primarily interested in those who are very good at algorithmic analysis, which is an essential skill for a data scientist.
A few sample questions for the algorithms part of the interview are given below:
- “Write code to generate iid draws from distribution X when we only have access to a random number generator.”
- “How would you find the top 5 highest-selling items from a list of order histories?”
- “Find all words which contain exactly two vowels in any list.”
These types of data science questions may require the recollection of theoretical concepts as well as problem-solving ability to quickly come up with a solution. Some of these questions will be twisted in such a way that the candidate would get confused and would not be able to answer it, even though he/she would have solved it if the question was asked directly. Thus, it is always best to practice such types of questions beforehand and work on different types of algorithms prior to attending the data scientist interview.
Coding
Being one of the biggest companies in the world and delivering products and services on a day-to-day basis, coding is the most important skill that is necessary to become a Data Scientist at Google. This means that you have to learn popular programming languages such as Python and R, as well as be proficient in writing queries using SQL for database manipulation.
Our analysis shows that a whopping 37.5% of the total questions asked in a Google Data Scientist interview is based on coding. Therefore, there is a lot of emphasis on the coding part of the interview and the candidate must be able to tackle head-on with good knowledge of the underlying concepts.
A few sample coding questions are given as follows:
- “Find the total AdWords earnings for each business type. Output the business types along with the total earnings.”

A possible solution to the question can be found here.
- “Find the price that a small handyman business is willing to pay per employee. Get the result based on the mode of the adword earnings per employee distribution. Small businesses are considered to have not more than one employee.”
A possible solution to the question can be found here.
Let us also discuss one coding question, the approach to solve it as well as the solution itself in complete detail. Consider the following question:
“Find the email activity rank for each user. Email activity rank is defined by the total number of emails sent. The user with the highest number of emails sent will have a rank of 1, and so on. Output the user, total emails, and their activity rank, and order records by the total emails in descending order. Choose a window function that will return a unique value (i.e., a unique percentile) even if multiple users have the same number of emails.”
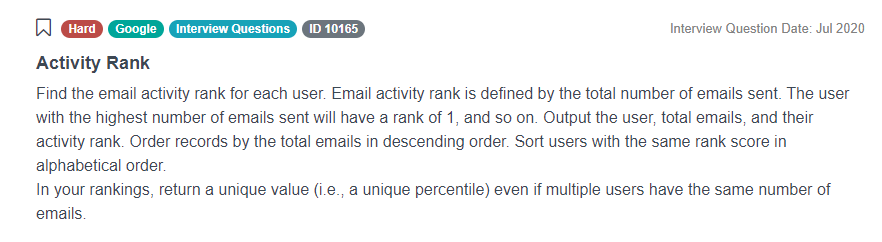
As we read this Google data scientist interview question, we can notice that there is a particular set of requirements - we are required to rank the activity of every user who sends emails. If a user has sent the highest number of mails, then that user will have a rank of 1.
We are required to sort the entire list of users, their corresponding number of sent emails and find out the activity ranks for all of them. If we encounter a particular set of users who have the same rank, we need to sort such users in alphabetical order. Finally, we are also required to return the percentile value for the rankings.
The main approach that we follow here is to utilize the powerful functions and clauses available in Postgres, in order to effectively arrive at our solution.
- First, we find the total number of emails sent by each user using the COUNT() function.
- Then, we group all the records by from_user.
- We use the ROW_NUMBER() function to order the records by total emails in descending order.
- Finally, we order the user with the same rank value alphabetically.
The entire solution in Postgres is given below:
SELECT from_user,
count(*) as total_emails,
row_number() OVER ( order by count(*) desc )
FROM google_gmail_emails
GROUP BY from_user
order by 3, 1These types of data science questions would test the candidate’s ability to utilize prominent data structures such as lists and string manipulations in order to arrive at the solution. Good knowledge of the available functions in SQL would definitely help in writing an efficient solution for these types of questions.
Behavioral
Behavioral questions are typically asked in data science interviews as it gives a fair idea of how the candidate would be able to work in a diverse environment. Such questions can also be used to understand if the candidate has excellent knowledge of the current affairs in the tech industry and any other related industries.
We can observe from the chart that around 21.9% of the questions asked in Google Data Scientist interviews are behavioral questions. This emphasizes the fact that Google tends to identify the best possible candidate in all aspects. Some might be very well versed in technical skills, but might not be able to communicate very well, or vice versa.
A few sample behavioral questions are given below:
- “Which data scientists do you admire most?”
- “Can you describe the process of data analysis?”
- “Why did you apply for this line of service?”
Such questions require quite a bit of involvement from the candidates to research about the current industry veterans and rising talent, who may be working on some revolutionary tech in the data science domain.
A few questions may also require the candidates to describe their personal interests or opinions, so as to build a good rapport with the interviewer. Academic and/or professional background may be touched upon in these types of questions, and usually there is quite a bit of back and forth that takes place.
Technical
Technical questions are quite closely related to the algorithms and/or coding questions, as they rely on the basic concepts learnt in the technical part of data science. These questions are generally based on the Python and R programming languages and the underlying concepts within them.
It can be observed from the chart above that technical questions account for around 9.4% of the total number of questions. This is due to the fact that the application of these technical questions are extremely high when it comes to data science, and therefore, we see a lot of coding interview questions that are built upon the technical questions. It is recommended to learn the underlying concepts and practice these questions beforehand, so as to easily crack them during the interviews.
Example technical questions for Google Data Scientist interviews are given below:
- “In which libraries for Data Science in Python and R, does your strength lie?”
- “Explain BQ, basic statistics and statistical sampling."
- “In R, how would you multiply all a[i,j] in a i rows j columns dataset?”
Such technical questions require adept knowledge of the libraries that are present in Python and R programming languages. Thorough practice of coding using these libraries will definitely help any candidate in tackling these technical questions in the data science interviews.
Product Sense
Finally, product sense based questions are usually meant to understand how a candidate sees the various aspects of a software/hardware product which may be released in the future. These types of questions may also help carve a path for a data scientist to pursue a career in software product management in the data science domain itself.
Our analysis shows that only 3.1% of product sense questions are asked in the Google data scientist interviews. This may be due to the fact that emphasis is placed more on the technical side of things, rather than product management.
Sample questions are given as follows:
- “How will you clean all the glass windows and doors for a city?”
- “What steps would you take to enhance YouTube’s business model?”
- “Why do you think that the Google search page is so mainly blank?”
As you can see, the above questions do not focus on any technical skills; rather, it gauges the candidate’s ability to identify the problem and come up with a solution which effectively manages the resources and time spent on the given work.
Technical Concepts Tested on Google Data Scientist Interview
We saw the emphasis of algorithms and coding questions in the Google Data Scientist interviews in the previous section. In this section, we will be delving into the technical concepts that are actually tested in these questions.
String Manipulation
The first concept that is evidently being tested on Google data scientist interview is that of string manipulation. We noticed that there are several questions that are being asked in the Google Data Science interviews which require the candidate to understand, analyze and code SQL queries and/or write Python code to manipulate strings.
One such example is given below:
“Shuffle the words in 'final.txt' and make a new file named 'wacky.txt'. Output the file contents in one column and the filename 'wacky.txt' in another column.”

A possible solution to the problem can be found here on our platform.
Joins
Secondly, we also observed a lot of focus is being given on questions that utilize joins. These types of questions require a lot of practice with SQL queries and can make or break an interview.
One such example is given below:
“Find the number of a user's friends' friend who are also the user's friend. Output the user id along with the count.”
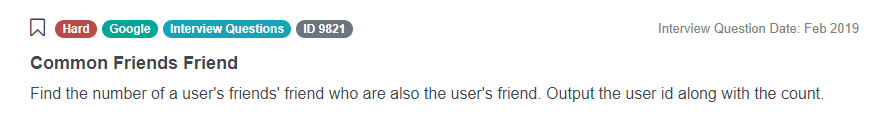
A possible solution to the problem can be found here on our platform.
Grouping and Tree Traversals
Finally, we also found a few questions that test grouping concepts in databases, or even tree traversals which seem to be very popular.
Two example questions for the same are given below:
“Find the total AdWords earnings for each business type. Output the business types along with the total earnings.” A possible solution to this can be found here on our platform.
“Given a binary tree, invert the tree and write the traversals for the same.”
In conclusion, the major technical concepts that are being tested are string manipulations, joins and grouping, with some emphasis on tree traversals as well. We highly recommend you to practice these types of questions before you attend your Google Data Scientist interviews.
Tips and Tricks to Ace the Google Data Scientist Interview
Finally, we speak a little bit about a few tips and tricks that you can use to prepare efficiently for your Google Data Scientist interview.
- Practice the standard algorithms and coding questions like string-based questions and questions utilizing joins, because our analysis showed us that there is a lot of emphasis given to string manipulation (especially questions on vowels) and joins-based questions (inner join, right join) in the coding/algorithms section of the interviews.
- Spend some time learning and practicing problems on trees and tree traversals, as we noticed that questions on trees and tree traversals are asked quite frequently in the interviews.
- Furthermore, study the theory and process behind data analysis as well as statistics, as we were also able to notice that questions on description of how data analysis works and some questions based on statistics and/or probability seemed to be popular in the interviews.
Also, check out our Ultimate Guide to Become a Data Scientist at Google.
Conclusion
To sum it up, we have explored and analyzed the various types of questions that are usually asked for the Data Scientist role at Google. We noticed that the whole interview process tends to be a long one, with multiple categories of questions being asked, at multiple difficulties as well.
Thorough practice of coding and algorithms will definitely help you in acing these interviews and securing your dream job at Google. StrataScratch definitely helps you in this aspect, so we urge you to make the best use of the platform to practice both coding and non-coding questions.
It is worth noting that good people skills and communication also plays a vital role in the interview process. Ensure that you speak well and politely to the interviewers.
We hope that this guide has helped you understand the ins and outs of how Google conducts their Data Science interviews. We wish you all the best in your preparations for the same!
Also, check out "Google Data Scientist Salary" to find all the details about earning your salary as a data scientist at Google.



