14 Different Data Science Job Titles

Categories:
 Written by:
Written by:Nathan Rosidi
A guide to all the data science job titles you can consider if you have a data science background.
There’s a multitude of jobs on the market requiring you to have a data science background. It can be confusing sometimes. It makes it difficult to know whether you’re over-or underqualified for a job. Sometimes, companies have overlapping job descriptions, or even their own specific understanding (and names) of what tasks a job should cover doesn’t help.
We’ll try to provide you with a guide that will help you make do with all the different data science job titles that require a data science background. Because many of these data science jobs require the same or very similar skills, we’ll start off by talking about the similarities between the jobs. We’ll also cover what qualifications and data science skills you need to land a job, as well as the example interview questions you could expect. Then we’ll talk about some specifics of the job description, technical skills, and the career trajectory, including the salaries.
Background for all Data Science Job Titles
How To Get it?
Data science is, by definition, the crossroads between several disciplines. It involves programming skills combined with mathematical and/or statistical knowledge and with business domain expertise. From this definition, we can answer where do the data scientists usually come from.
Their formal education usually involves a degree in computer science, mathematics, statistics, economics, or any similar quantitative field. For some data science jobs, a degree in a humanistic field could also be nice to have, especially if the job is more people-behavior-oriented.
Depending on the job seniority, you could be required to hold a Master’s degree or even a Ph.D.
What Skills Do I Need?
It depends on plenty of factors, and of course, there are differences between various data science jobs. However, there are some skills that you need to have for virtually every job that requires a data science background. The only difference is to what extent you’ll use that skill at your job.

- Working with data – collect, organize, clean, and manipulate it
- Coding – usually SQL, Python, or R, sometimes also Java, C++...
- Visualizing data – usually using BI tools such as Tableau, Power BI, Looker…
- Database modeling – understand how databases work
- Statistical analysis – apply it in data analysis to gain the insights
- Mathematical knowledge – apply it to data analysis to calculate metrics
Here's the detailed article Data Science Skills where you'll find the skills that are in highest demand.
Sounds Fine. How Do I Get a Job?
You get a job by acing a job interview. That involves getting the right answers to the questions you get asked.
Again, the questions you get will vary depending on the job, its seniority, the company, and whatnot. However, by looking at the skills all the data science jobs require to some degree, you can narrow down the types of questions.
For sure, you’ll get some coding questions. A question such as this one by Amazon is a good example:
Last Updated: April 2019
Calculate the ratio of the total spend a customer spent on each order. Output the customer’s first name, order details, and ratio of the order cost to their total spend across all orders.
Assume each customer has a unique first name (i.e., there is only 1 customer named Karen in the dataset) and that customers place at most only 1 order a day.
Percentages should be represented as decimals
Answer:
SELECT c.first_name,
o.order_details,
o.total_order_cost / sum(o.total_order_cost) OVER (PARTITION BY
c.first_name)::float AS percentage_total_cost
FROM orders o
JOIN customers c ON c.id = o.cust_idOr maybe you could get a question similar to the one from Airbnb:
Last Updated: February 2018
You are given a table named airbnb_host_searches that contains data for rental property searches made by users. Determine the minimum, average, and maximum rental prices for each popularity-rating bucket. A popularity-rating bucket should be assigned to every record based on its number_of_reviews (see rules below).
The host’s popularity rating is defined as below: • 0 reviews: "New" • 1 to 5 reviews: "Rising" • 6 to 15 reviews: "Trending Up" • 16 to 40 reviews: "Popular" • More than 40 reviews: "Hot"
Tip: The id column in the table refers to the search ID.
Output host popularity rating and their minimum, average and maximum rental prices. Order the solution by the minimum price.
Answer:
WITH hosts AS
(SELECT concat(price, room_type, host_since, zipcode,
number_of_reviews) AS host_id,
number_of_reviews,
price
FROM airbnb_host_searches
GROUP BY 1,2,3)
SELECT host_popularity AS host_pop_rating,
min(price) AS min_price,
avg(price) AS avg_price,
max(price) AS max_price
FROM
(SELECT CASE
WHEN number_of_reviews = 0 THEN 'New'
WHEN number_of_reviews BETWEEN 1 AND 5 THEN 'Rising'
WHEN number_of_reviews BETWEEN 6 AND 15 THEN 'Trending Up'
WHEN number_of_reviews BETWEEN 16 AND 40 THEN 'Popular'
WHEN number_of_reviews > 40 THEN 'Hot'
END AS host_popularity,
price
FROM hosts) a
GROUP BY host_pop_ratingIf your job is more statistics-heavy, you could get questions like this one from Facebook:

“What is the expectation of the variance?”
Answer:
Variance describes how much a random variable differs from its expected mean. Let's say we have a random variable X. The variance of X then can be expressed mathematically as:
Var(X)=E[(X−μ)2]=1N∑Ni=1(xi−μ)2
From the equation above, a closed-form solution can be derived to compute the variance of X in a simpler way:
Var(X)=E(X2)−E(X)2
The original question is to find out the expectation of the variance. We can write this mathematically as:
E(Var(X))
=E(E(X2)−E(X)2)
=E(E(X2))−E(E(X)2)
If we have a constant random variable, we know that:
E(X)=Xand
E(E(X))=E(X)
Hence, we can further continue to simplify the equation above as follows:
E(E(X2))−E(E(X)2)
=E(X2)−E(X)2
=Var(X)
Thus, the expectation of the variance is the variance itself.
Modeling is also one of the often skills used in these jobs. So maybe you’ll have to answer the question like this from Square:

“How do you test whether a new credit risk scoring model works? What data would you look at?”
Apart from preparing interview questions, working on your CV and cover letter is also important to stand out from others in an interview. To assist you, we’ve discussed how to write a perfect data science cover letter here.
Also, check out this very specific and practical guide on how to get a Data Science job.
Career Trajectory
There’s no one and only one way how you can become a data scientist. It depends on your education and previous working experience. However, people usually start as data analysts. Then, according to their interests and skills, they generally move in two directions: one is working more with data and data infrastructure, the other is more focused on data analysis.
You can see this trajectory in the illustration below. Some jobs sometimes require other education such as business or humanistic degree.
All those paths can lead to you becoming a data scientist. You can move in multiple directions; it all depends on your company, career moves, interests, etc.
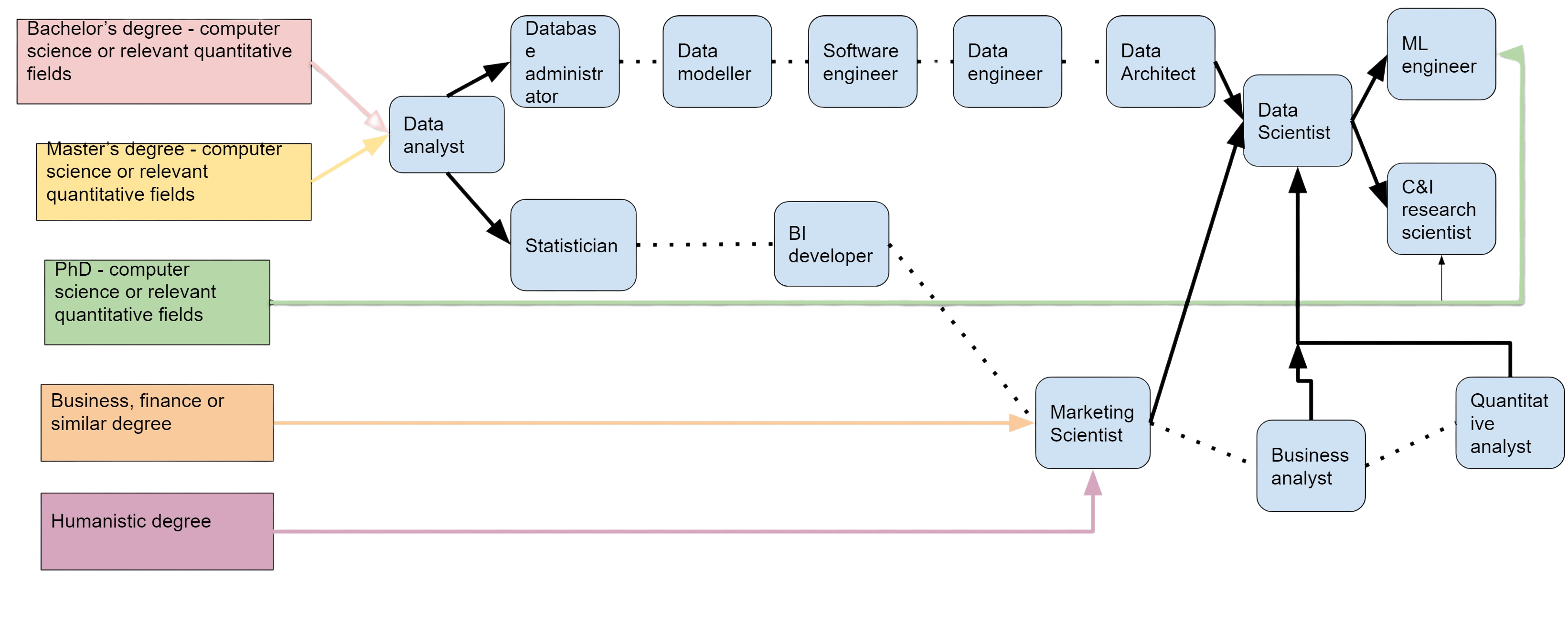
How Much Can I Earn?
Here’s the list of the data science job titles you can find below in the jobs breakdown. The table shows the data science job title and the average annual total compensation. We’ve ordered the jobs according to the career trajectory above. That way, you’ll be able to follow how your pay could rise if you take a typical path of becoming a data scientist.
| No | Job title | Average total compensation ($USD) |
| 1 | Data analyst | $70k |
| 2 | Database administrator | $84k |
| 3 | Data modeler | $94k |
| 4 | Software engineer | $108k |
| 5 | Data engineer | $113k |
| 6 | Data architect | $119k |
| 7 | Statistician | $89k |
| 8 | Business intelligence (BI) developer | $92k |
| 9 | Marketing scientist | $94k |
| 10 | Business analyst | $77k |
| 11 | Quantitative analyst | $112k |
| 12 | Data scientist | $139k |
| 13 | Computer & information research scientist | $142k |
| 14 | Machine learning engineer | $189k |
Check out our previous article How Much Do Data Scientists Make to find out about salaries and how they are influenced by several factors.
14 Different Data Science Job Titles Breakdown
The General Description of a Data Scientist
Job Description
A data scientist is a person who uses mathematical, statistical, and programming skills to gain insights from data. They will gather, organize, clean, and analyze data. This part is the same as with data analysts. However, they are more forward-looking and prediction-oriented. They will use the data to build the machine learning models. They help them make predictions by finding trends, patterns, and behaviors in the available data. They do it to solve business problems and increase the company’s performance in terms of sales, clients’ experience, costs, revenue, etc.
This is the most general role description which covers most of the skills you’ll need as someone with the data science background. All other jobs you’ll find below are derivatives of this job, requiring different technical focuses of a data science knowledge and skills.
Skills Required
Programming Languages
- SQL
- R
- Python
- Java/JavaScript
- C/C++/C#
Platform Tools
- Data science and machine learning platforms (e.g. Jupyter Notebooks, MATLAB, KNIME, MS Azure-learning Studio, IBM Watson Machine Learning, etc.)
- BI tools (e.g. Tableau, Power BI, Looker, QlikSense, etc.)
- Relational databases (e.g. MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, HIVE, Snowflake, etc.)
- Cloud databases (e.g. Amazon Web Service, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Programming
- Data manipulation, analysis, and visualization
- Data modeling
- Model building, testing, and deploying
- Machine learning
- AI
- Cloud computing
- APIs
- Statistics and mathematics
Data Analyst
Technical Focus
Data analysis and reporting.
Job Description
This data science job title is required to gather, organize, and clean data when needed. After that, they are required to perform regular and ad-hoc analyses and provide reports. That way, they help make business decisions and unlock answers to some business problems. Data analysts are usually required to visualize data and communicate the results of their analyses. In a way, we can say that data analysts are using data to describe past and present, while data scientists use it to predict the future.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Same as data scientist, but more data-analysis oriented so SQL is the primary language with Python used for statistical work and automation
Platform Tools
- Same as data scientist, but more heavily using programming platforms like Jupyter notebooks and SQL IDEs
Technical Skills
- Same as data scientist, but focused on data manipulation and analysis
Data Engineer
Technical Focus
Data infrastructure, data cleaning, data preparation and manipulation.
Job Description
The data engineers’ main task is to develop and maintain data infrastructure. Its purpose is to transform data into an “analyzable” format and make such data available to data scientists and data analysts. That means they have to gather, maintain, manipulate, and load data for others to use. Data engineers are more focused on extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data than data analysts and data scientists.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Scala
- Go
Platform Tools
- ETL tools (e.g. Microsoft SSIS, XPlenty, Talend, Cognos Data Manager, etc.)
Technical Skills
- ETL
Machine Learning Engineer
Technical Focus
Model building and deploying to production
Job Description
This data science job title requires you to design, build, and maintain artificial intelligence (AI) software and algorithms that will automate predictive models and enable machines to function without being given instructions for every action. To do that, you’ll have to organize and analyze data that you will use for training and validating the machine learning model. This description shows the machine learning engineer is the same as a data scientist, except focused on both building and deploying the machine learning models.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Julia
- Scala
- Go
Platform Tools
- Application frameworks (e.g. Django, Flask, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Software architecture
Research Scientist
Technical Focus
Research of computing, user, and business problem. Trying to understand deep rooted issues and behaviors of users, products, and features.
Job Description
This data science job title is more on a theoretical and research level than others we’ve gone through. Research scientists explore computing problems and then improve existing algorithms or write new ones to solve those problems. They also create new computing languages, tools, and software that will improve how the computers work and the users’ experience with them.
Usually, you’ll be working in one of three fields focused on hardware, software, or robotics.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Deep knowledge of programming theory and principles
Platform Tools
- No specific tools required due to theoretical nature of the job
Technical Skills
- Hardware engineering
- Software architecture
Marketing Scientist
Technical Focus
Data science applied to marketing and sales data, solving business problems related to marketing and sales (for example, field force sizing and marketing ROI)
Job Description
The person who works under this data science job title is the one who approaches marketing data using scientific methods. You’ll be doing that to support the decision-making by correctly interpreting data, finding a common pattern in data that reveals customer behavior. To achieve that, you’ll run experiments to confirm or dismiss the hypotheses. This is basically the same as the data scientist, but you work with the marketing type of data, such as e-mail engagement data.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Same as data scientist, but primarily SQL for data querying, and Python/R for statistical and econometric modeling
Platform Tools
- Same as a data scientist, but more marketing-data oriented with marketing analytics tools such as Google Analytics or Heap Analytics
Technical Skills
- Marketing and business knowledge
Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
Technical Focus
Building graphical dashboards
Job Description
The BI developer is a data-savvy engineer who develops and maintains BI interfaces and works in BI tools. Those are tools that allow querying and visualizing data, creating dashboards, regular and ad-hoc reports. In a way, this is a combination of a data engineer (ETL), data analyst (analysis & reporting), and software engineer (software development).
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Same as a data scientist, but focused on data-querying so SQL is a primary language with Python and R used for more complex applications and statistical modeling
Platform Tools
- Same as a data scientist, but more BI-oriented (dashboarding tools such as Tableau)
Technical Skills
- ETL/ELT
- Data warehousing
- Software development
- Business background
Business Analyst
Technical focus
Similar to a data analyst but can also be focused on internal reporting like finance and improving the company’s systems and processes.
Job Description
This data science job title assesses the company’s systems and processes. They analyze them and come up with solutions, usually in the shape of improved or new systems and other technical improvements. The purpose of this is to lower the costs and improve the company’s efficiency and decision-making, which should lead to earning more money.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Generally only SQL
Platform Tools
- Business analysis tools (e.g. Modern Requirements, Axure, Enterprise Architecture, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Project management
- Software testing
- Business background
Data Modeler
Technical Focus
Data modeling and database design
Job Description
Their job is to design, improve and maintain data models, which they then translate to database implementation. They do that with the purpose of improving data availability and database performance in general. To do that, they need to cooperate with data administrators and data architects.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Generally only SQL
Platform Tools
- Data modeling (e.g. DbSchema, ER/Studio, Draw.io, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Database design
- Data warehousing
- ETL/ELT
Database Administrator
Technical Focus
Database administration and maintenance
Job Description
This data science job title is in charge of, well, database administration. This means they work with data modelers and data architects in database implementation. Only they are more focused on practical and technical issues rather than conceptual. Their job is to ensure the availability of databases, which includes allowing (or not) access to databases, backup and restore data, ensuring data security and integrity, and high database performance.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Generally only SQL
Platform Tools
- Database administration (e.g. PGAdmin4, SQL Server Management Studio, phpMyAdmin, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Database design
- Data warehousing
- ETL/ELT
- Database administration
Data Architect
Technical Focus
Architecture and infrastructure of data management
Job Description
Compared to data modeler and database administrator, the data architect is a data science job title that requires a high-level point of view. The data architect’s job is to have in mind the company’s business needs and develop the complete architecture of data management. This doesn’t involve just databases but laying out the framework for how the data will be collected, used, modeled, retrieved, secured. In general, this means providing an architecture that will be there from the point data enters the company to the point it leaves it.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Same as a data scientist, but primarily SQL since they’re focused on data and databases, with Python and Java used for building applications when needed
Platform Tools
- Database administration (e.g. PGAdmin4, SQL Server Management Studio, phpMyAdmin, etc.)
- Big data (Apache Hadoop, Cassandra, MongoDB, etc.)
- Data modeling (e.g. DbSchema, ER/Studio, Draw.io, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Database design
- Data warehousing
- ETL/ELT
- Database administration
Software Engineer
Technical focus
Software development
Job Description
This data science job title is relatively similar to a data engineer. The main difference is they are usually not concerned with data infrastructure, like data engineers. Instead, they build software on top of this data infrastructure, which allows the end-users to use the underlying data and data infrastructure.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Scala
Platform Tools
- DevOps (e.g. Docker, Kubernetes, etc.)
- Continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) (e.g. Jenkins, CircleCI, Bamboo, GitLab, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Software architecture, developing, and testing
- Database design
- Data warehousing
- ETL/ELT
- Database administration
Statistician
Technical Focus
Statistical analysis of data
Job Description
This job title is basically the same as a data scientist. The difference is it's focused only on the statistics part of the data scientist job. They, too, analyze data, apply statistical methods to data, and identify patterns and trends that will provide business insight and support decision-making.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Same as data scientist, but more statistics and data-analysis oriented (many more R users in this field but Python is also popular)
Platform Tools
- Same as data scientist, but more use of statistical analysis tools (e.g., SPSS, MATLAB, SAS)
Technical Skills
- Same as data scientist, but more statistics and data-analysis oriented
Quantitative Analyst
Technical Focus
Data scientist focused on financial data
Job Description
This job is basically the same as a data scientist but focused on financial data. Quantitative analysts (or “quants”) will analyze data and build models to help the company understand financial markets and their trends. Based on those analyses and models, the company will decide on its investments, FX and equity trading, loan approvals, etc.
Additional Skills Required Compared to Data Scientists
Programming Languages
- Same as data scientist, but focused on Python/R for quant model protyping
Platform Tools
- Automated trading platforms (MetaTrader4, eToro, etc.)
Technical Skills
- Financial mathematics
- Risk management
Summary
Data science is a vast and ever-developing field. This list of the 14 different Data Science job titles we gave you is not an ultimate list because the new data science job types are being created almost daily. It also depends on the company’s organization and size how they will call a certain position. This can mean merging several job types into one or breaking down one job type into several sub-types and specializations, all performed by several people.
However, these data science job titles cover most often jobs you could do with a data science background. Every job description is specific, but we’re sure you’ll find suitable job interview questions for all of them on our site. You can choose between various coding and non-coding questions, so help yourself.
Share


